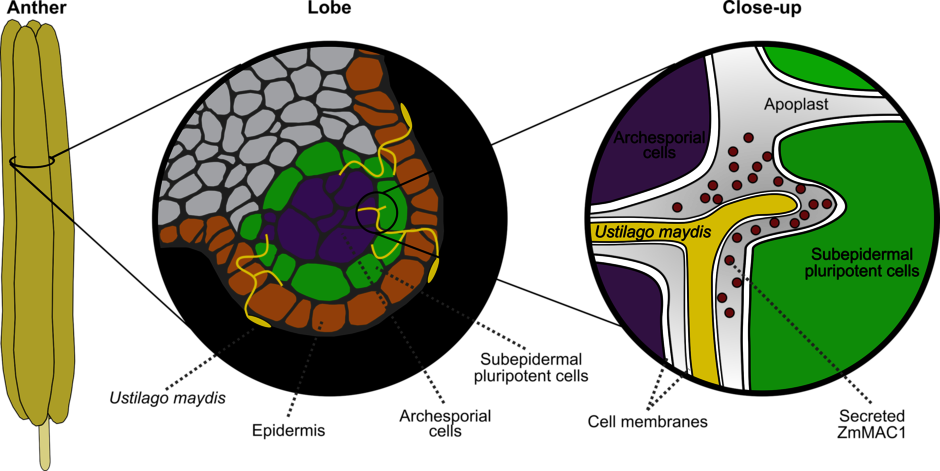
Despite their recognition as key players in defense, development, physiology, and cell-to-cell communication, only a few small secreted proteins have been discovered and characterized in crop plants thus far.
Our goal is to identify new small apoplasmic proteins. Candidate proteins are selected from proteomic data and screened at macroscopic, microscopic, and molecular levels to determine their impact on development and pathogenicity using the U. maydis-based Trojan horse strategy, which we established. Further protein characterization by biochemical and genetic approaches are used to elucidate interacting partners and to identify affected pathways.