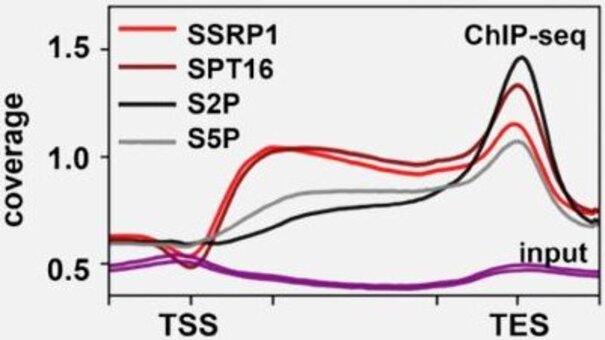
In eukaryotic cells, the large genomic DNA is packaged with histones and other proteins into chromatin. The compaction of the DNA provided by chromatin generally represses DNA-dependent processes such as the transcription of genes. During transcript elongation by RNA polymerase II a variety of factors facilitates transcript synthesis. Using the Arabidopsis model system, we examine how these factors are involved in gene expression, development and plant responses to changing environmental conditions. In addition, we are interested in the interplay with co-transcriptional events and the mechanism of mRNA export from the nucleus. Towards these goals we employ approaches from the fields of molecular and cellular biology as well as biochemistry and genetics.
.