Various processing steps including 5´capping, splicing and 3´processing occur essentially during RNA polymerase II transcription, converting pre-mRNAs into mature mRNAs. Before mRNAs can be translated in the cytosol they have to be exported from the cell nucleus through nuclear pore complexes (NPCs). The regulated nucleo-cytosolic transport assures that only properly processed mRNAs are passed on to the cytosol for translation. Therefore, the export of mRNAs represents a critical step in gene expression. Accordingly, a variety of mRNA export factors is recruited to the mRNA co-transcriptionally that render the mature transcript export-competent (Ehrnsberger et al., 2019a) (externer Link, öffnet neues Fenster). A central player in mRNA export is the THO/TREX complex, consisting of the THO core subunits that associate with additional factors including the UAP56 RNA helicase, ALY-/UIF-like proteins and MOS11 (Sørensen et al., 2017 (externer Link, öffnet neues Fenster)). Finally, adaptor proteins such as ALY recruit the soluble mRNA export receptor (ExR, which is unknown in plants) that mediates translocation of the export-competent mRNP through the NPC.
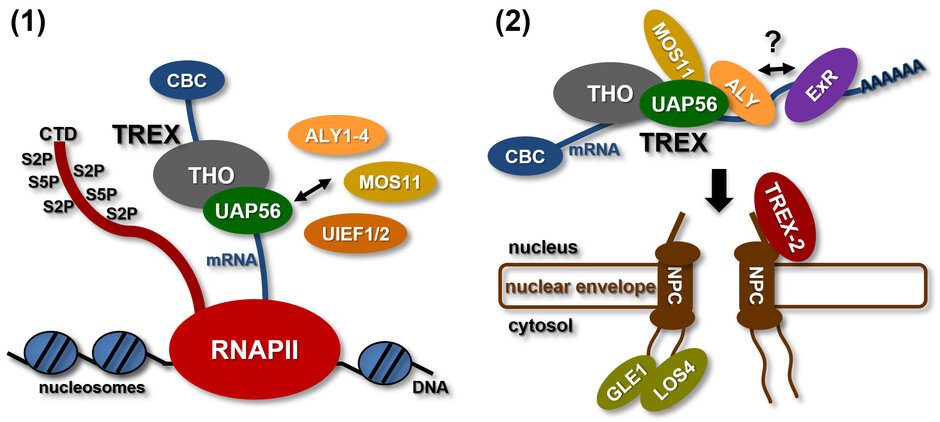
Arabidopsis UAP56 is a DEAD-box helicase and two neighbouring genes encode an identical protein that is ubiquitously expressed and localises primarily to the nucleoplasm in root and leaf cells. Recombinant UAP56 binds both to ssRNA and dsRNA, and it has RNA-stimulated ATPase activity as well as ATP-dependent RNA helicase activity resulting in the unwinding of dsRNA (Kammel et al., 2013 (externer Link, öffnet neues Fenster)). UAP56 interacts directly with ALY/UIEF proteins and MOS11, and therefore may be involved in the recruitment of these export factors.

Export factors of the ALY family are more diversified in plants than in other organisms and Arabidopsis expresses four ALY proteins termed ALY1-4. ALY1 and ALY2 are closely related and likewise ALY3 and ALY4 share a high degree of amino acid sequence identity. In vitro RNA-binding assays demonstrate that in addition to the central RNA recognition motif (RRM) of ALY1 both the N- and C-terminal domains contribute to the RNA interactions. Plants defective in single ALY genes as well as double-mutant plants exhibit basically wild type appearance. However, quadruple mutant plants defective in the expression of all four ALY genes (4xaly) display various vegetative and reproductive abnormalities including small size, reduced root growth and decreased fertility (Pfaff et al., 2018 (externer Link, öffnet neues Fenster)). In line with this observation, mRNA export is reduced in 4xaly plants as evident from nuclear accumulation of polyadenylated mRNAs detected by in situ hybridisation with fluorescently labelled oligo(dT) probes. A second group of mRNA export factors termed UIEF1/2 cooperate with the ALY proteins to facilitate translocation of mRNAs through NPCs to the cytosol (Ehrnsberger et al., 2019b (externer Link, öffnet neues Fenster)).

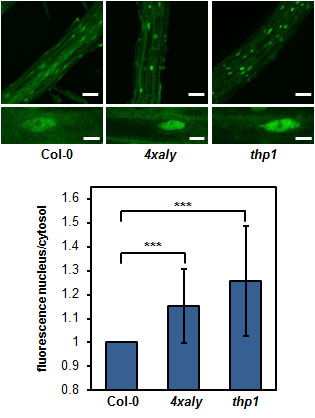
These results demonstrate that proper plant development requires efficient nucleo-cytosolic transport of mRNAs, whose mechanism we intend to study in more detail in future experiments.
